Difference between revisions of "ViSUS Docker Deployment"
(→Content of the image) |
(→Content of the image) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
when you run you docker image. | when you run you docker image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === How to customize the list of datasets on your server === | ||
For example if you want to use your own [[ViSUS configuration file]] you can run the container as following: | For example if you want to use your own [[ViSUS configuration file]] you can run the container as following: | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 7 February 2018
Contents
Quick start
Start your Docker and login into your account. If you don't have installed follow these instructions: Docker Documentation
To log in from your terminal:
docker login Username: your_username Password: XXXX
Now pull the ViSUS image:
docker pull visus/visus
This image contains:
- the ViSUS Server
- configuration files (see ViSUS configuration file)
- a simple 2D web viewer
- some tools to convert data (see ViSUS Convert).
Run the image:
docker run -it --rm -p 8080:80 visus/visus
Check if the server is running:
curl -v "http://localhost:8080/mod_visus?action=list"
You will get a list of the current datasets on the server.
Content of the image
This image contains folders with configuration files and utilities. The folders of interest are under /home/visus:
- config, it contains the visus server.config (see ViSUS configuration file)
- apache2, it contains the apache2 config files that you can use for security settings (see ViSUS Server)
- visus, it contains visus tool (see ViSUS Convert) to convert data to IDX format
The user can map those folders locally and edit them adding:
-v local_directory:docker_directory
when you run you docker image.
How to customize the list of datasets on your server
For example if you want to use your own ViSUS configuration file you can run the container as following:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 -v $PWD/config:/home/visus/config
Note: The server needs to be able to read and write the configuration file, so make sure that your server.config has the right privileges. For example:
chmod 766 /path/to/your/server.config
Making the configuration file writable will allow to add datasets dynamically using the action add_dataset (see ViSUS Server).
If you also want to customize the apache security (e.g. change the users) you can run the command to mount also the apache2 directory as following:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 -v $PWD/config:/home/visus/config -v $PWD/apache2:/home/visus/apache2 visus/visus
Use ViSUS convert from the Docker container
The ViSUS tools executables (see ViSUS Convert) are contained in the image under /usr/local/visus/bin.
For example, if you want to use the tools to convert a raw dataset using your docker deployment you can do it as follow.
Mount a folder that contains your raw data and your converted idx data as follow:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 -v /full/path/to/your/raw/:/home/visus/datasets/raw -v /full/path/to/your/idx/:/home/visus/datasets/idx visus/visus
Check that your container is running correctly (using docker ps) and take note of the Container ID.
Now run a bash session on this container using:
docker exec -it <id_from_docker_ps> /bin/bash
From this bash session you can use your ViSUS converter to convert your data (just mounted in the container) as described in ViSUS Convert.
Experimental: Web Viewer
You can preview and navigate you data on the server using the webviewer using your browser at the URL: http://localhost:8080
Here is a picture of the viewer:
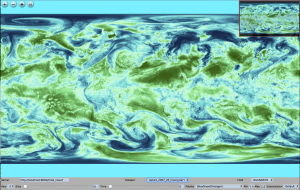
With the commands on the bottom bar you can:
- change server
- set a slice (if using a 3D dataset)
- set a timestep
- set palettes and min-max range
- choose a field of the selected dataset
Note: this component is experimental and under development.
